Publications
Filter
Year
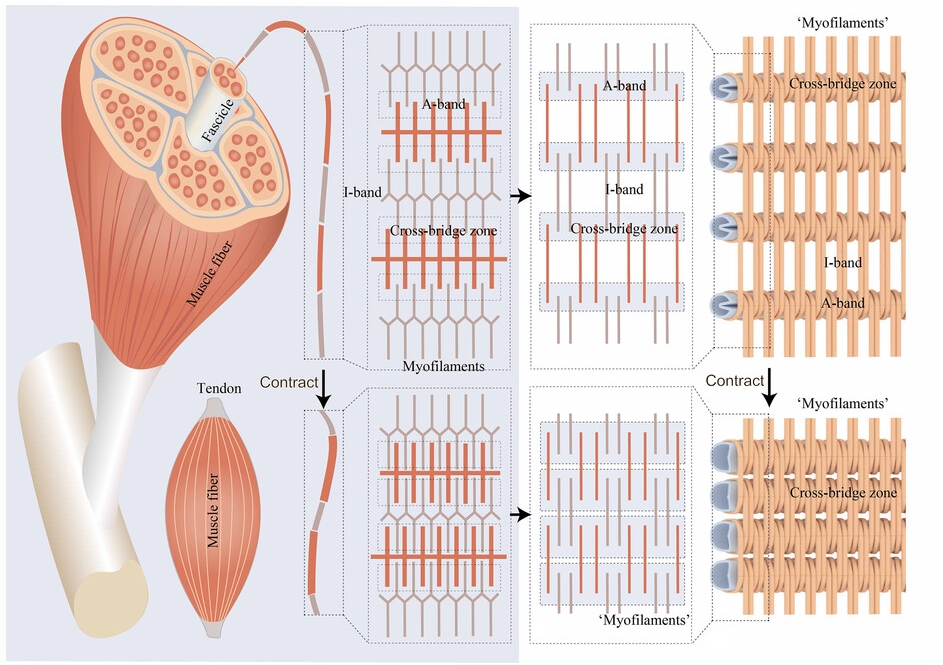
Fluid‐Driven High‐Performance Bionic Artificial Muscle with Adjustable Muscle Architecture
Fluid-Driven ExoMuscle mimics sarcomere structures with adjustable architecture, achieving up to 0.9 MPa actuation stress and 10.94 kW/kg power density. This bionic muscle enhances bio-robotics and wearable robots, combining efficiency with adaptability to human anatomy. Read more
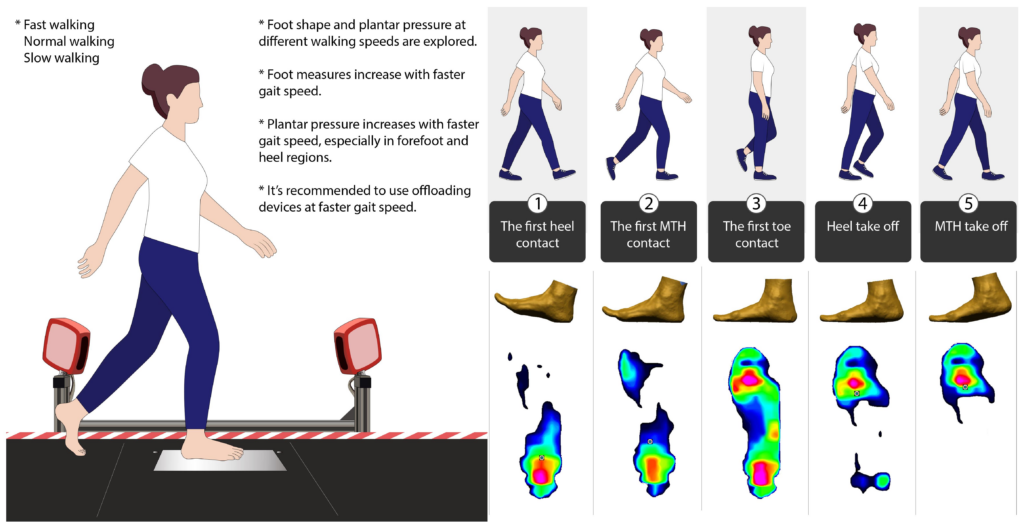
Analysis of Diabetic Foot Deformation and Plantar Pressure Distribution of Women at Different Walking Speeds
This study analyzes foot deformation and plantar pressure in diabetic patients at varying walking speeds. It shows increased pressure in forefoot and heel at higher speeds, stressing the need for suitable footwear and offloading devices to protect against injury and ensure comfort. Read more
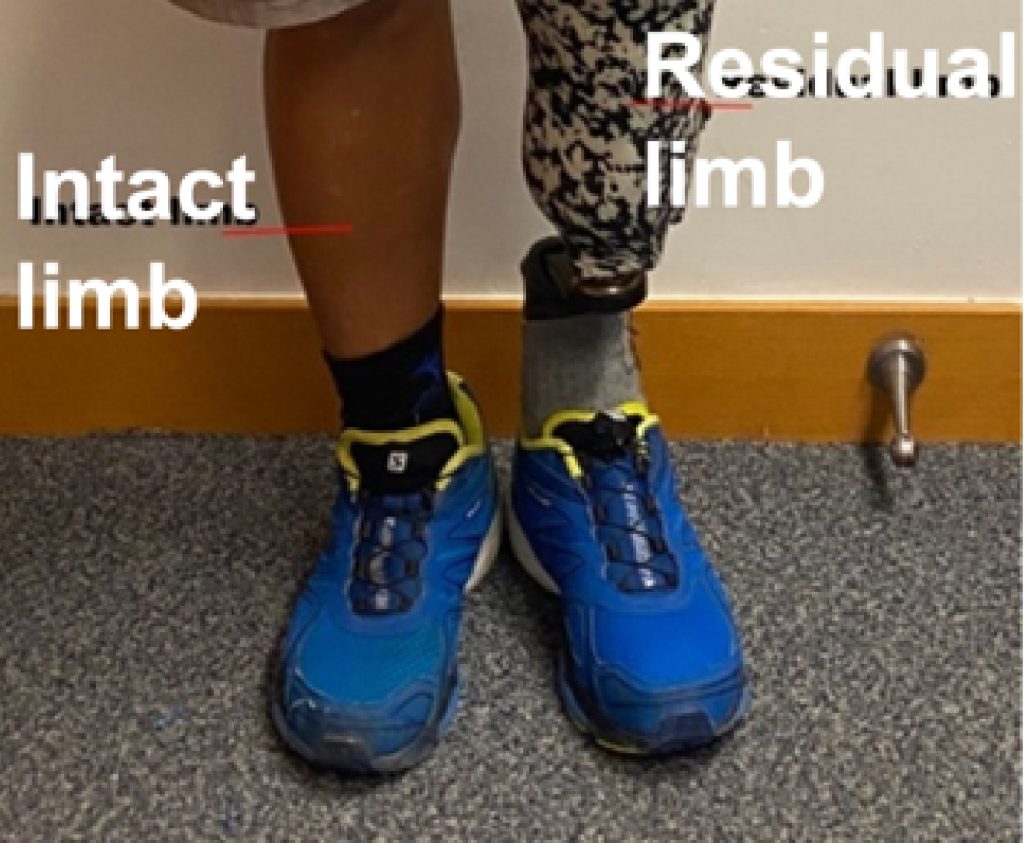
Biomechanical Analysis Of Unilateral Transtibial Amputees Using Prosthetic Foot During Treadmill Walking At Varying Slopes: 1721
This study aimed to investigate the effect of the prosthetic foot used by unilateral transtibial amputees during different walk tasks by utilizing biomechanical analysis. Read more
Surface electromyography (sEMG) biofeedback posture training improves the physical and mental health of early adolescents with mild scoliosis: A qualitative study
This study explores a biofeedback posture training program for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, highlighting its ability to improve paraspinal muscle symmetry and reduce curve progression. It also examines how the program enhances posture correction and quality of life for adolescents through subjective experiences. Read more

Immediate Effects of Posture Correction Girdle on Adolescents with Early Scoliosis.
This study explores a posture correction girdle for adolescents with early scoliosis, using radiographic imaging and 3D body scanning. Findings reveal positive effects, including reduced spinal curves and improved postural balance, suggesting alternative treatment options beyond observation. Read more

A zwitterionic silver nanoparticle-incorporating injectable hydrogel with a durable and efficient antibacterial effect for accelerated wound healing
Antibacterial wound dressing is essential for inflammation control and accelerated wound healing. This study investigates polyzwitterion-functionalized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with enhanced antibacterial performance in an injectable wound dressing hydrogel. Read more

Preliminary wear trial of anisotropic textile brace designed for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
This study introduces a semi-rigid brace for adolescent scoliosis patients, achieving effective spinal correction with enhanced comfort. Preliminary wear trials indicate its performance matches original designs, while offering superior user experience. Read more
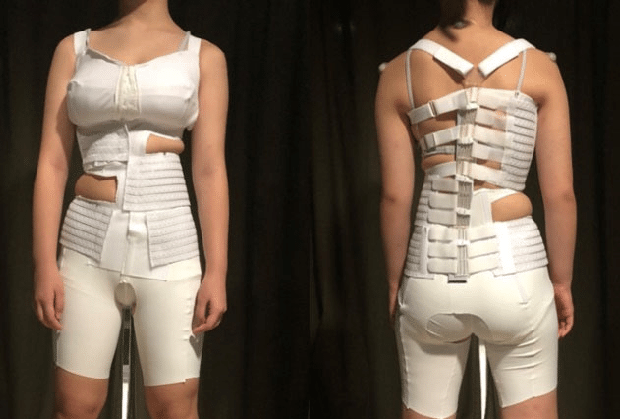

Design and fabrication of anisotropic textile brace for exerting corrective forces on spinal curvature
This study focuses on the fabrication of an anisotropic textile brace that exerts corrective forces based on the three-point pressure system to treat scoliosis, which is a medical condition that involves deformity of the spine. Read more

Highly Transparent, Mechanical, and Self-Adhesive Zwitterionic Conductive Hydrogels with Polyurethane as Cross-Linker for Wireless Strain Sensors
Zwitterionic hydrogels excel in flexibility, strength, and sensory sensitivity for wearable sensors. Their superior adhesion supports applications in robotics and prosthetics, providing reliable real-time mechanotransduction detection without additional adhesives. Read more

Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
